Same Side Exterior Angles Definition Math

One is an exterior angle outside the parallel lines and one is an interior angle inside the parallel lines.
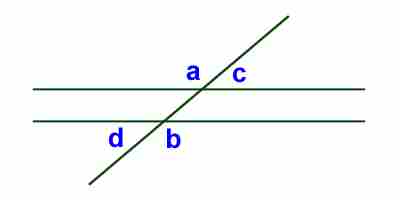
Same side exterior angles definition math. An exterior angle is the angle between any side of the polygon and a line extended from the next sideHere is an example to helpIf you draw an triangle the angles inside it are interior angles. 1 and 4 is one pair of alternate exterior angles and the other pair is 2 and 3. When two lines are crossed by another line the Transversal a pair of angles.
So Side Angle Side SAS means one side the angle next to that side and then the side next to that angle. Alternate exterior angles lie outside the lines cut by the transversal. From the figure 1 2 7 8 are Exterior angles.
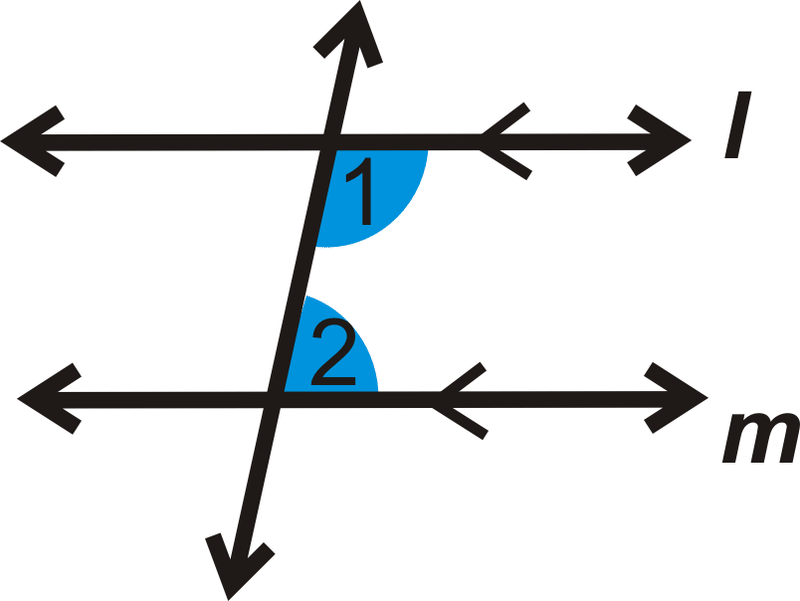
Two angles correspond or relate to each other by being on the same side of the transversal. Since alternate interior and alternate exterior angles are congruent and since linear pairs of angles are supplementary same side angles are supplementary. The same side of what.
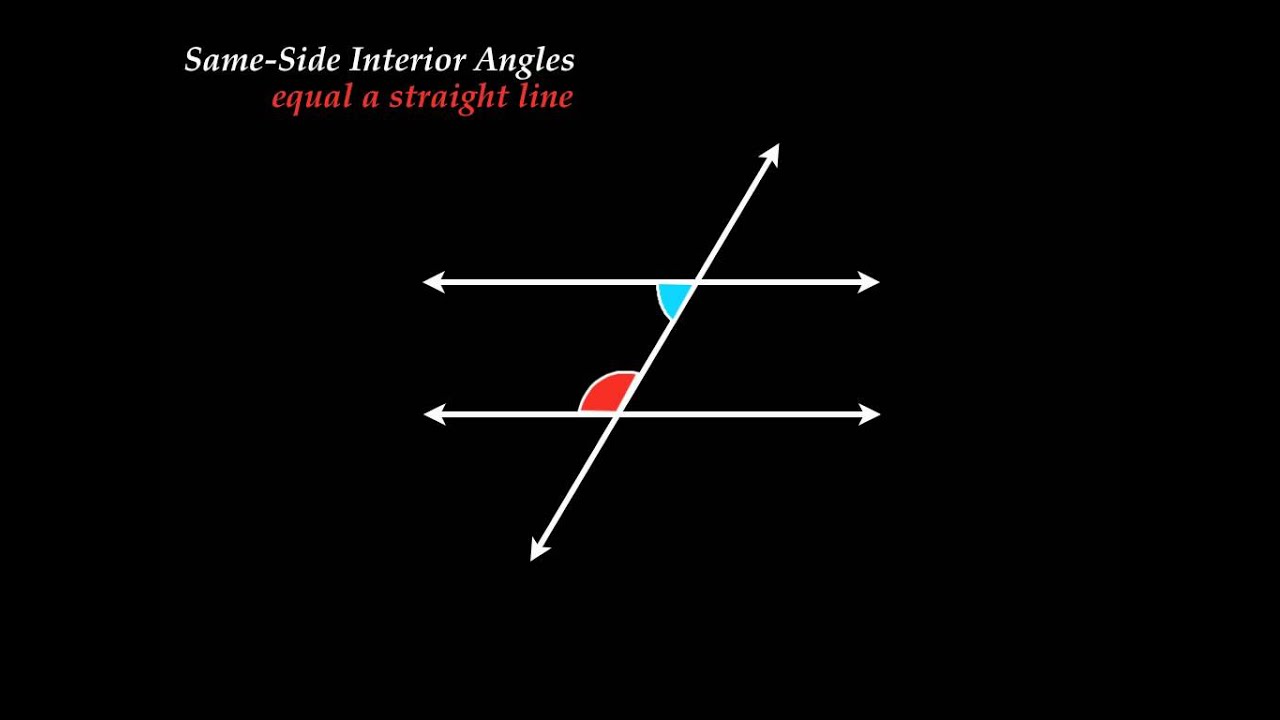
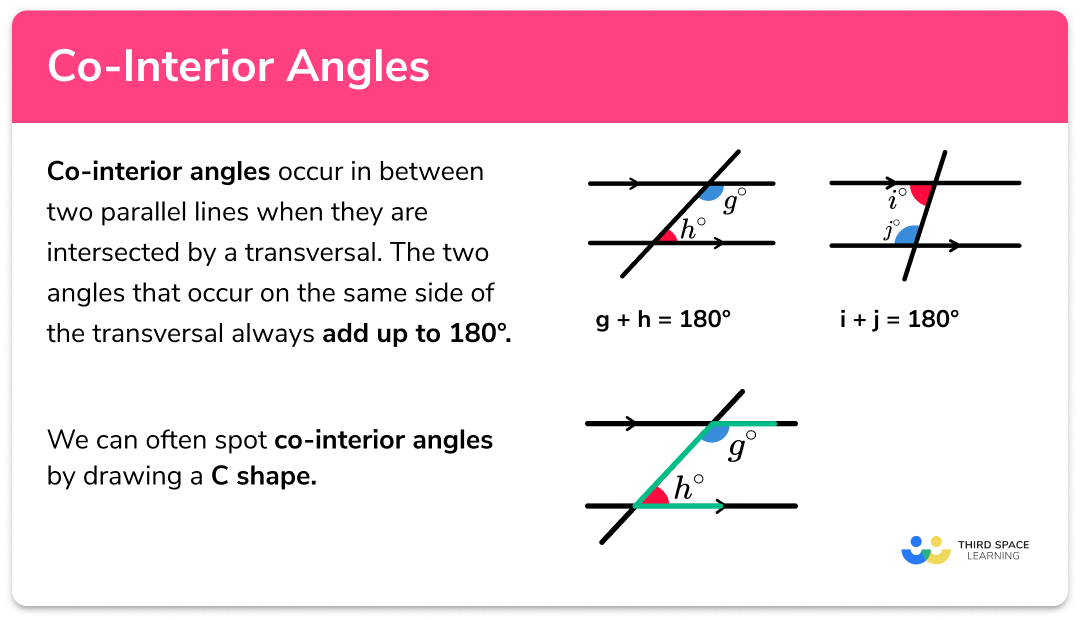
This means that the interior angles which are on the same side of the transversal are supplementary. So we all know that a triangle is a 3-sided figure with three interior angles. The corresponding pair of angles.
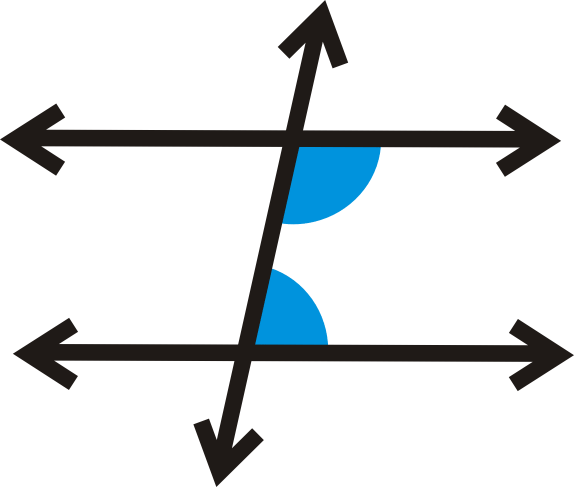
Each pair of these angles are outside the parallel lines and on the same side of the transversal. You will see that the angles combine to a full 360 circle. Same-side interior angles are a pair of angles on one side of a transversal line and on the inside of the two lines being intersected.
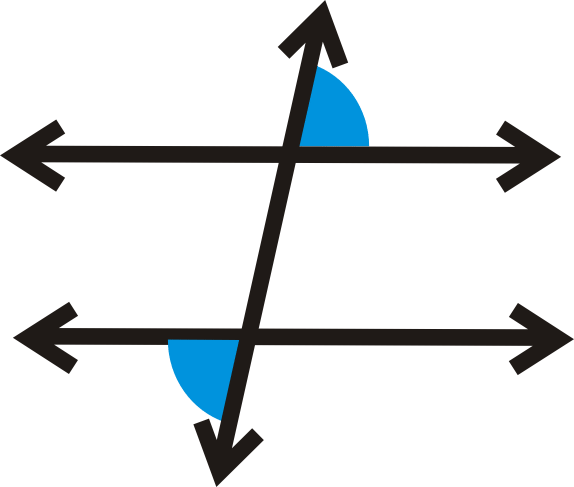
Angles that are on the opposite side of the transversal are called alternate angles. Alternate Exterior Angles Alternate exterior angles are the pair of angles on the outer side of the two parallel lines but on the opposite side of the transversal. But on opposite sides of the transversal.